Evaluation Quick Start
In this walkthrough, you will evaluate a chain over a dataset of examples. To do so, you will:
- Create a dataset
- Define the system to evaluate
- Configure and run the evaluation
- Review the resulting traces and evaluation feedback in LangSmith
Prerequisites
This walkthrough assumes you have already installed LangChain and openai and configured your environment to connect to LangSmith.
- Python
- TypeScript
pip install -U "langchain langchain_openai"
yarn add langchain @langchain/openai
Then configure your API key.
export LANGCHAIN_API_KEY=<your api key>
1. Create a dataset
Upload a dataset to LangSmith to use for evaluation. For this example, we will upload a pre-made list of input examples.
For more information on other ways to create and use datasets, check out the how-to guides.
- Python SDK
- TypeScript SDK
from langsmith import Client
# Inputs are provided to your model, so it know what to generate
dataset_inputs = [
"a rap battle between Atticus Finch and Cicero",
"a rap battle between Barbie and Oppenheimer",
# ... add more as desired
]
# Outputs are provided to the evaluator, so it knows what to compare to
# Outputs are optional but recommended.
dataset_outputs = [
{"must_mention": ["lawyer", "justice"]},
{"must_mention": ["plastic", "nuclear"]},
]
client = Client()
dataset_name = "Rap Battle Dataset"
# Storing inputs in a dataset lets us
# run chains and LLMs over a shared set of examples.
dataset = client.create_dataset(
dataset_name=dataset_name,
description="Rap battle prompts.",
)
client.create_examples(
inputs=[{"question": q} for q in dataset_inputs],
outputs=dataset_outputs,
dataset_id=dataset.id,
)
import { Client } from "langsmith";
// Inputs are provided to your model, so it know what to generate
const datasetInputs = [
{question: "a rap battle between Atticus Finch and Cicero"},
{question: "a rap battle between Barbie and Oppenheimer"},
// ... add more as desired
];
// Outputs are provided to the evaluator, so it knows what to compare to
// Outputs are optional but recommended.
const datasetOutputs = [
{ must_mention: ["lawyer", "justice"] },
{ must_mention: ["plastic", "nuclear"] },
];
const client = new Client();
const datasetName = "Rap Battle Dataset";
// Storing inputs in a dataset lets us
// run chains and LLMs over a shared set of examples.
const dataset = await client.createDataset(datasetName, {
description: "Rap battle prompts.",
});
await client.createExamples({
inputs: datasetInputs,
outputs: datasetOutputs,
datasetId: dataset.id,
});
2. System to evaluate
- Python
- TypeScript
The run_on_dataset test runner can evaluate any function. This includes any Runnable LangChain component.
If your system is stateful (for instance, if it has chat memory) you can instead provide a constructor for your system that creates a new instance for each example record in the dataset. If your system is stateless, you can directly pass it in without worrying about any constructors.
- Custom function
- Runnable
- Agent
- LLM or Chat Model
- Custom class
import openai
# You evaluate any arbitrary function over the dataset.
# The input to the function will be the inputs dictionary for each example.
def predict_result(input_: dict) -> dict:
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": input_["question"]}]
response = openai.chat.completions.create(messages=messages, model="gpt-3.5-turbo")
return {"output": response}
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo", temperature=0)
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([("human", "Spit some bars about {question}.")])
chain = prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()
from langchain.agents import AgentExecutor, create_openai_functions_agent
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", "Spit some bars about the topic\n\n{agent_scratchpad}"),
("user", "{question}"),
]
)
@tool
def get_encouragement(request: str) -> str:
"""Get some encouragement."""
return "You can do it!"
tools = [get_encouragement]
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo")
# Since chains and agents can be stateful (they can have memory),
# create a constructor to pass in to the run_on_dataset method.
def create_agent():
agent = create_openai_functions_agent(
llm,
tools=[get_encouragement],
prompt=prompt,
)
return AgentExecutor(agent=agent, tools=tools)
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo", temperature=0)
# If your predictor is stateful (e.g. it has memory),
# You can create a new instance of the predictor for each row in the dataset.
class MyPredictor:
def __init__(self):
self.state = 0
def predict(self, input_: dict) -> dict:
if self.state > 0:
raise ValueError("This predictor is stateful and can only be called once."")
self.state += 1
return {"output": f"Bar Bar Bar {self.state}"}
def create_object() -> MyPredictor:
predictor = MyPredictor()
# Return the function that will be called on the next row
return predictor.predict
The runOnDataset test runner can evaluate any function. This includes any Runnable LangChain component.
If your system is stateful (for instance, if it has chat memory) you can instead provide a constructor for your system that creates a new instance for each example record in the dataset. If your system is stateless, you can directly pass it in without worrying about any constructors.
- Custom function
- Runnable
- Agent
- LLM or Chat Model
import OpenAI from "openai";
const client = new OpenAI();
async function predictResult({ question }: { question: string }) {
const messages = [{ "role": "user", "content": question }];
const output = await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-3.5-turbo",
messages: messages
});
return { output };
}
import { StringOutputParser } from "@langchain/core/output_parsers";
import { ChatPromptTemplate } from "@langchain/core/prompts";
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
const llm = new ChatOpenAI({ modelName: "gpt-3.5-turbo", temperature: 0 });
const prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.fromMessages([
["human", "Spit some bars about {question}."],
]);
// This is what we will evaluate
const chain = prompt.pipe(llm).pipe(new StringOutputParser());
import { ChatPromptTemplate } from "@langchain/core/prompts";
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
import { AgentExecutor, createOpenAIFunctionsAgent } from "langchain/agents";
import { DynamicStructuredTool } from "@langchain/core/tools";
import { z } from "zod";
const prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.fromMessages([
["system", "Spit some bars about the topic\n\n{agent_scratchpad}"],
["user", "{question}"]
]);
const getEncouragementTool = new DynamicStructuredTool({
name: "get_encouragement",
description: "Get some encouragement.",
schema: z.object({
request: z.string()
}),
func: async ({ request }) => {
return "You can do it!";
}
});
const tools = [getEncouragementTool];
const llm = new ChatOpenAI({modelName: "gpt-3.5-turbo"});
// Define a constructor function to create an agent
async function createAgent() {
const agent = await createOpenAIFunctionsAgent({llm, tools, prompt});
return new AgentExecutor({agent, tools});
}
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
const llm = new ChatOpenAI({modelName: "gpt-3.5-turbo", temperature: 0});
3. Evaluate
- Python
- TypeScript
LangChain provides a convenient run_on_dataset and async arun_on_dataset method to generate predictions (and traces) over a dataset. When a RunEvalConfig is provided, the configured evalutors will be applied to the predictions as well to generate automated feedback.
Below, configure evaluation for some custom criteria. The feedback will be automatically logged within LangSmith.
For more information on evaluators you can use off-the-shelf, check out the pre-built evaluators docs or the reference documentation for LangChain's evalution module. For more information on how to write a custom evaluator, check out the custom evaluators guide.
- Custom function
- Runnable
- Agent
- LLM or Chat Model
- Custom class
from langchain.smith import RunEvalConfig, run_on_dataset
from langsmith.evaluation import EvaluationResult, run_evaluator
@run_evaluator
def must_mention(run, example) -> EvaluationResult:
prediction = run.outputs.get("output") or ""
required = example.outputs.get("must_mention") or []
score = all(phrase in prediction for phrase in required)
return EvaluationResult(key="must_mention", score=score)
eval_config = RunEvalConfig(
custom_evaluators=[must_mention],
# You can also use a prebuilt evaluator
# by providing a name or RunEvalConfig.<configured evaluator>
evaluators=[
# You can specify an evaluator by name/enum.
# In this case, the default criterion is "helpfulness"
"criteria",
# Or you can configure the evaluator
RunEvalConfig.Criteria("harmfulness"),
RunEvalConfig.Criteria(
{
"cliche": "Are the lyrics cliche?"
" Respond Y if they are, N if they're entirely unique."
}
),
],
)
client.run_on_dataset(
dataset_name=dataset_name,
llm_or_chain_factory=predict_result,
evaluation=eval_config,
verbose=True,
project_name="custom-function-test-1",
# Any experiment metadata can be specified here
project_metadata={"version": "1.0.0"},
)
from langchain.smith import RunEvalConfig, run_on_dataset
from langsmith.evaluation import EvaluationResult, run_evaluator
@run_evaluator
def must_mention(run, example) -> EvaluationResult:
prediction = run.outputs.get("output") or ""
required = example.outputs.get("must_mention") or []
score = all(phrase in prediction for phrase in required)
return EvaluationResult(key="must_mention", score=score)
eval_config = RunEvalConfig(
custom_evaluators=[must_mention],
# You can also use a prebuilt evaluator
# by providing a name or RunEvalConfig.<configured evaluator>
evaluators=[
# You can specify an evaluator by name/enum.
# In this case, the default criterion is "helpfulness"
"criteria",
# Or you can configure the evaluator
RunEvalConfig.Criteria("harmfulness"),
RunEvalConfig.Criteria(
{
"cliche": "Are the lyrics cliche?"
" Respond Y if they are, N if they're entirely unique."
}
),
],
)
client.run_on_dataset(
dataset_name=dataset_name,
llm_or_chain_factory=chain,
evaluation=eval_config,
verbose=True,
project_name="runnable-test-1",
# Any experiment metadata can be specified here
project_metadata={"version": "1.0.0"},
)
from langchain.smith import RunEvalConfig, run_on_dataset
from langsmith.evaluation import EvaluationResult, run_evaluator
@run_evaluator
def must_mention(run, example) -> EvaluationResult:
prediction = run.outputs.get("text") or ""
required = example.outputs.get("must_mention") or []
score = all(phrase in prediction for phrase in required)
return EvaluationResult(key="must_mention", score=score)
eval_config = RunEvalConfig(
custom_evaluators=[must_mention],
# You can also use a prebuilt evaluator
# by providing a name or RunEvalConfig.<configured evaluator>
evaluators=[
# You can specify an evaluator by name/enum.
# In this case, the default criterion is "helpfulness"
"criteria",
# Or you can configure the evaluator
RunEvalConfig.Criteria("harmfulness"),
RunEvalConfig.Criteria(
{
"cliche": "Are the lyrics cliche?"
" Respond Y if they are, N if they're entirely unique."
}
),
],
)
client.run_on_dataset(
dataset_name=dataset_name,
llm_or_chain_factory=create_agent,
evaluation=eval_config,
verbose=True,
project_name="agent-test-1",
# Any experiment metadata can be specified here
project_metadata={"version": "1.0.0"},
)
from langchain.smith import RunEvalConfig, run_on_dataset
from langsmith.evaluation import EvaluationResult, run_evaluator
@run_evaluator
def must_mention(run, example) -> EvaluationResult:
prediction = run.outputs["generations"][0][0]["text"]
required = example.outputs.get("must_mention") or []
score = all(phrase in prediction for phrase in required)
return EvaluationResult(key="must_mention", score=score)
eval_config = RunEvalConfig(
custom_evaluators=[must_mention],
# You can also use a prebuilt evaluator
# by providing a name or RunEvalConfig.<configured evaluator>
evaluators=[
# You can specify an evaluator by name/enum.
# In this case, the default criterion is "helpfulness"
"criteria",
# Or you can configure the evaluator
RunEvalConfig.Criteria("harmfulness"),
RunEvalConfig.Criteria(
{
"cliche": "Are the lyrics cliche?"
" Respond Y if they are, N if they're entirely unique."
}
),
],
)
client.run_on_dataset(
dataset_name=dataset_name,
llm_or_chain_factory=llm,
evaluation=eval_config,
verbose=True,
project_name="chatopenai-test-1",
)
from langchain.smith import RunEvalConfig, run_on_dataset
from langsmith.evaluation import EvaluationResult, run_evaluator
@run_evaluator
def must_mention(run, example) -> EvaluationResult:
prediction = run.outputs.get("output") or ""
must_mention = example.outputs.get("must_mention") or []
score = all(phrase in prediction for phrase in must_mention)
return EvaluationResult(key="must_mention", score=score)
eval_config = RunEvalConfig(
custom_evaluators=[must_mention],
# You can also use a prebuilt evaluator
# by providing a name or RunEvalConfig.<configured evaluator>
evaluators=[
# You can specify an evaluator by name/enum.
# In this case, the default criterion is "helpfulness"
"criteria",
# Or you can configure the evaluator
RunEvalConfig.Criteria("harmfulness"),
RunEvalConfig.Criteria(
{
"cliche": "Are the lyrics cliche?"
" Respond Y if they are, N if they're entirely unique."
}
),
],
)
client.run_on_dataset(
dataset_name=dataset_name,
# We are passing the "factory" function in this case.
llm_or_chain_factory=create_object,
evaluation=eval_config,
verbose=True,
project_name="custom-class-test-1",
)
LangChain provides a convenient runOnDataset function to trace and evaluate your system over a dataset. When a RunEvalConfig is provided, the configured evalutors will be applied to the predictions as well to generate automated feedback.
Below, configure evaluation for some custom criteria. The feedback will be automatically logged within LangSmith.
For more information on evaluators you can use off-the-shelf, check out the pre-built evaluators docs or the reference documentation for LangChain's evalution module. For more information on how to write a custom evaluator, check out the custom evaluators guide.
- Custom function
- Runnable
- Agent
- LLM or Chat Model
import { RunEvalConfig, runOnDataset } from "langchain/smith";
import { Run, Example } from "langsmith";
import { EvaluationResult } from "langsmith/evaluation";
// You can define any custom evaluator as a function
// The 'run' contains the system outputs (and other trace information).
// The 'example' contains the dataset inputs and outputs.
const mustMention = async ({
run,
example,
}: {
run: Run;
example?: Example;
}): Promise<EvaluationResult> => {
// Check whether the prediction contains the required phrases
const mustMention: string[] = example?.outputs?.must_contain ?? [];
// Assert that the prediction contains the required phrases
const score = mustMention.every((phrase) =>
run?.outputs?.output.includes(phrase)
);
return {
key: "must_mention",
score: score,
};
};
const formatEvaluatorInputs = function ({
rawInput, // dataset inputs
rawPrediction, // model outputs
rawReferenceOutput, // dataset outputs
}) {
return {
input: rawInput.question,
prediction: rawPrediction?.output,
reference: `Must mention: ${rawReferenceOutput?.must_mention ?? [].join(", ")}`,
};
};
const evalConfig: RunEvalConfig = {
// Custom evaluators can be user-defined RunEvaluator's
customEvaluators: [mustMention],
// Prebuilt evaluators
evaluators: [
{
evaluatorType: "labeled_criteria",
criteria: "helpfulness",
feedbackKey: "helpfulness",
// The off-the-shelf evaluators need to know how to interpret the data
// in the dataset and the model output.
formatEvaluatorInputs
},
{
evaluatorType: "criteria",
criteria: {
cliche: "Are the lyrics cliche?"
},
feedbackKey: "is_cliche",
formatEvaluatorInputs
},
],
};
await runOnDataset(predictResult, datasetName, {
evaluationConfig: evalConfig,
// You can manually specify a project name
// or let the system generate one for you
// projectName: "custom-function-test-1",
projectMetadata: {
// Experiment metadata can be specified here
version: "1.0.0",
},
});
import { RunEvalConfig, runOnDataset } from "langchain/smith";
import { Run, Example } from "langsmith";
import { EvaluationResult } from "langsmith/evaluation";
// The 'run' contains the system outputs (and other trace information).
// The 'example' contains the dataset inputs and outputs.
const mustMention = async ({
run,
example,
}: {
run: Run;
example?: Example;
}): Promise<EvaluationResult> => {
// Check whether the prediction contains the required phrases
const mustMention: string[] = example?.outputs?.must_contain ?? [];
// Assert that the prediction contains the required phrases
const score = mustMention.every((phrase) =>
run?.outputs?.output.includes(phrase)
);
return {
key: "must_mention",
score: score,
};
};
const formatEvaluatorInputs = function ({
rawInput, // dataset inputs
rawPrediction, // model outputs
rawReferenceOutput, // dataset outputs
}) {
return {
input: rawInput.question,
prediction: rawPrediction?.output,
reference: `Must mention: ${rawReferenceOutput?.must_mention ?? [].join(", ")}`,
};
};
const evalConfig: RunEvalConfig = {
// Custom evaluators can be user-defined RunEvaluator's
customEvaluators: [mustMention],
// Prebuilt evaluators
evaluators: [
{
evaluatorType: "labeled_criteria",
criteria: "helpfulness",
feedbackKey: "helpfulness",
// The off-the-shelf evaluators need to know how to interpret the data
// in the dataset and the model output.
formatEvaluatorInputs
},
{
evaluatorType: "criteria",
criteria: {
cliche: "Are the lyrics cliche?"
},
feedbackKey: "is_cliche",
formatEvaluatorInputs
},
],
};
await runOnDataset(chain, datasetName, {
evaluationConfig: evalConfig,
// You can manually specify a project name
// or let the system generate one for you
projectName: "custom-runnable-test-1",
projectMetadata: {
// Experiment metadata can be specified here
version: "1.0.0",
},
});
import { RunEvalConfig, runOnDataset } from "langchain/smith";
import { Run, Example } from "langsmith";
import { EvaluationResult } from "langsmith/evaluation";
// The 'run' contains the system outputs (and other trace information).
// The 'example' contains the dataset inputs and outputs.
const mustMention = async ({
run,
example,
}: {
run: Run;
example?: Example;
}): Promise<EvaluationResult> => {
// Check whether the prediction contains the required phrases
const mustMention: string[] = example?.outputs?.must_contain ?? [];
// Assert that the prediction contains the required phrases
const score = mustMention.every((phrase) =>
run?.outputs?.output.includes(phrase)
);
return {
key: "must_mention",
score: score,
};
};
const formatEvaluatorInputs = function ({
rawInput, // dataset inputs
rawPrediction, // model outputs
rawReferenceOutput, // dataset outputs
}) {
return {
input: rawInput.question,
prediction: rawPrediction?.output,
reference: `Must mention: ${rawReferenceOutput?.must_mention ?? [].join(", ")}`,
};
};
const evalConfig: RunEvalConfig = {
// Custom evaluators can be user-defined RunEvaluator's
customEvaluators: [mustMention],
// Prebuilt evaluators
evaluators: [
{
evaluatorType: "labeled_criteria",
criteria: "helpfulness",
feedbackKey: "helpfulness",
// The off-the-shelf evaluators need to know how to interpret the data
// in the dataset and the model output.
formatEvaluatorInputs
},
{
evaluatorType: "criteria",
criteria: {
cliche: "Are the lyrics cliche?"
},
feedbackKey: "is_cliche",
formatEvaluatorInputs
},
],
};
await runOnDataset(createAgent, datasetName, {
evaluationConfig: evalConfig,
// You can manually specify a project name
// or let the system generate one for you
projectName: "custom-agent-test-1",
projectMetadata: {
// Experiment metadata can be specified here
version: "1.0.0",
},
});
import { RunEvalConfig, runOnDataset } from "langchain/smith";
import { Run, Example } from "langsmith";
import { EvaluationResult } from "langsmith/evaluation";
// You can define any custom evaluator as a function
// The 'run' contains the system outputs (and other trace information).
// The 'example' contains the dataset inputs and outputs.
const mustMention = async ({
run,
example,
}: {
run: Run;
example?: Example;
}): Promise<EvaluationResult> => {
// Check whether the prediction contains the required phrases
const mustMention: string[] = example?.outputs?.must_contain ?? [];
// Assert that the prediction contains the required phrases
const score = mustMention.every((phrase) =>
run?.outputs?.output.includes(phrase)
);
return {
key: "must_mention",
score: score,
};
};
const formatEvaluatorInputs = function ({
rawInput, // dataset inputs
rawPrediction, // model outputs
rawReferenceOutput, // dataset outputs
}) {
return {
input: rawInput.input,
prediction: rawPrediction?.output,
reference: `Must mention: ${rawReferenceOutput?.must_mention ?? [].join(", ")}`,
};
};
const evalConfig: RunEvalConfig = {
// Custom evaluators can be user-defined RunEvaluator's
customEvaluators: [mustMention],
// Prebuilt evaluators
evaluators: [
{
evaluatorType: "labeled_criteria",
criteria: "helpfulness",
feedbackKey: "helpfulness",
// The off-the-shelf evaluators need to know how to interpret the data
// in the dataset and the model output.
formatEvaluatorInputs
},
{
evaluatorType: "criteria",
criteria: {
cliche: "Are the lyrics cliche?"
},
feedbackKey: "is_cliche",
formatEvaluatorInputs
},
],
};
await runOnDataset(llm, datasetName, {
evaluationConfig: evalConfig,
// You can manually specify a project name
// or let the system generate one for you
projectName: "chatopenai-test-1",
projectMetadata: {
// Experiment metadata can be specified here
version: "1.0.0",
},
});
4. Review Results
The evaluation results will be streamed to a new test project linked to your "Rap Battle Dataset". You can view the results by clicking on the link printed by the run_on_dataset function or by navigating to the Datasets & Testing page, clicking "Rap Battle Dataset", and viewing the latest test run.
There, you can inspect the traces and feedback generated from the evaluation configuration.
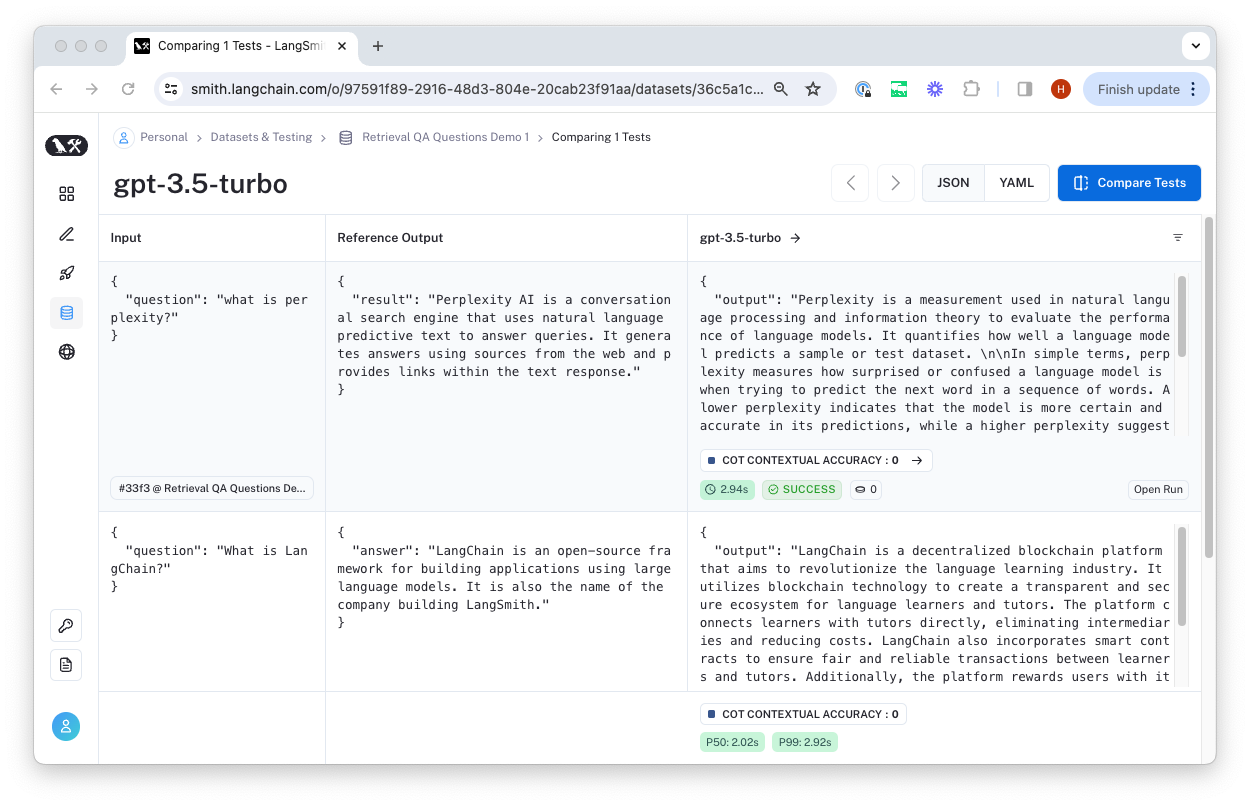
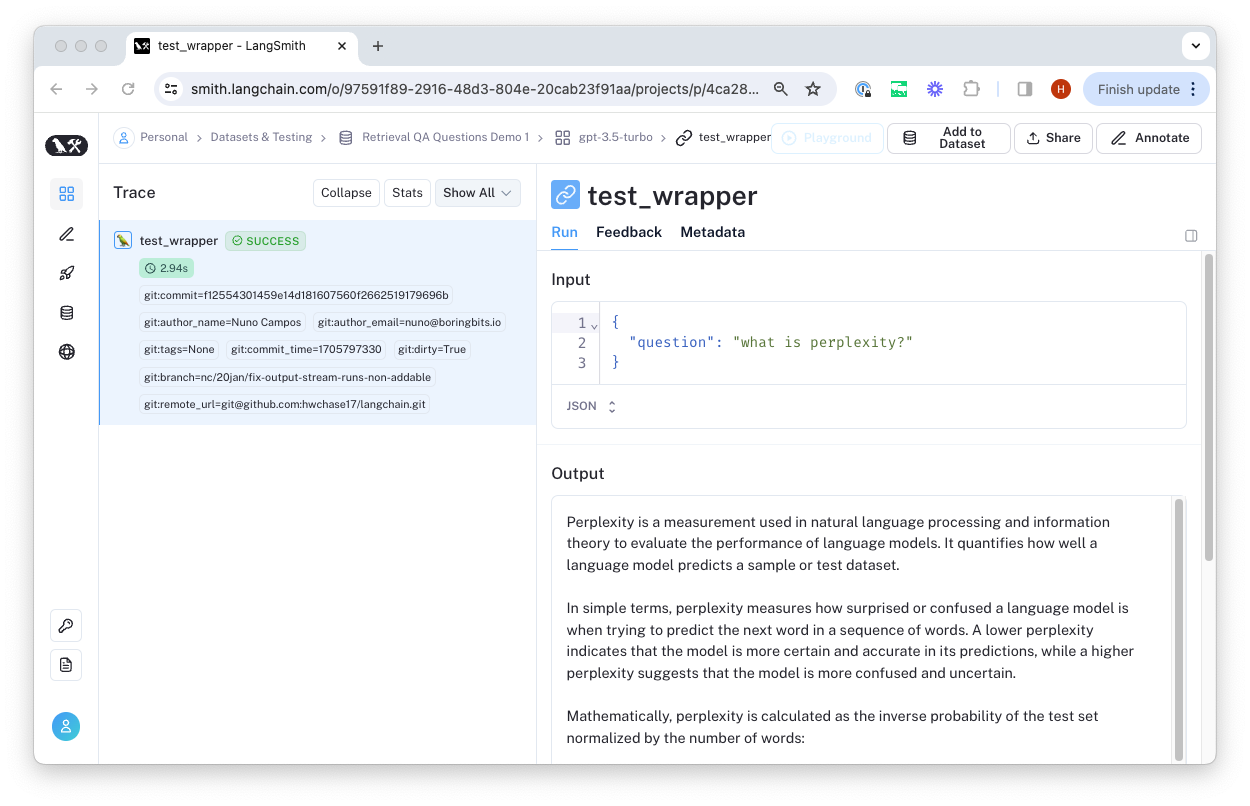
You can click "Open Run" to view the trace and feedback generated for that example.
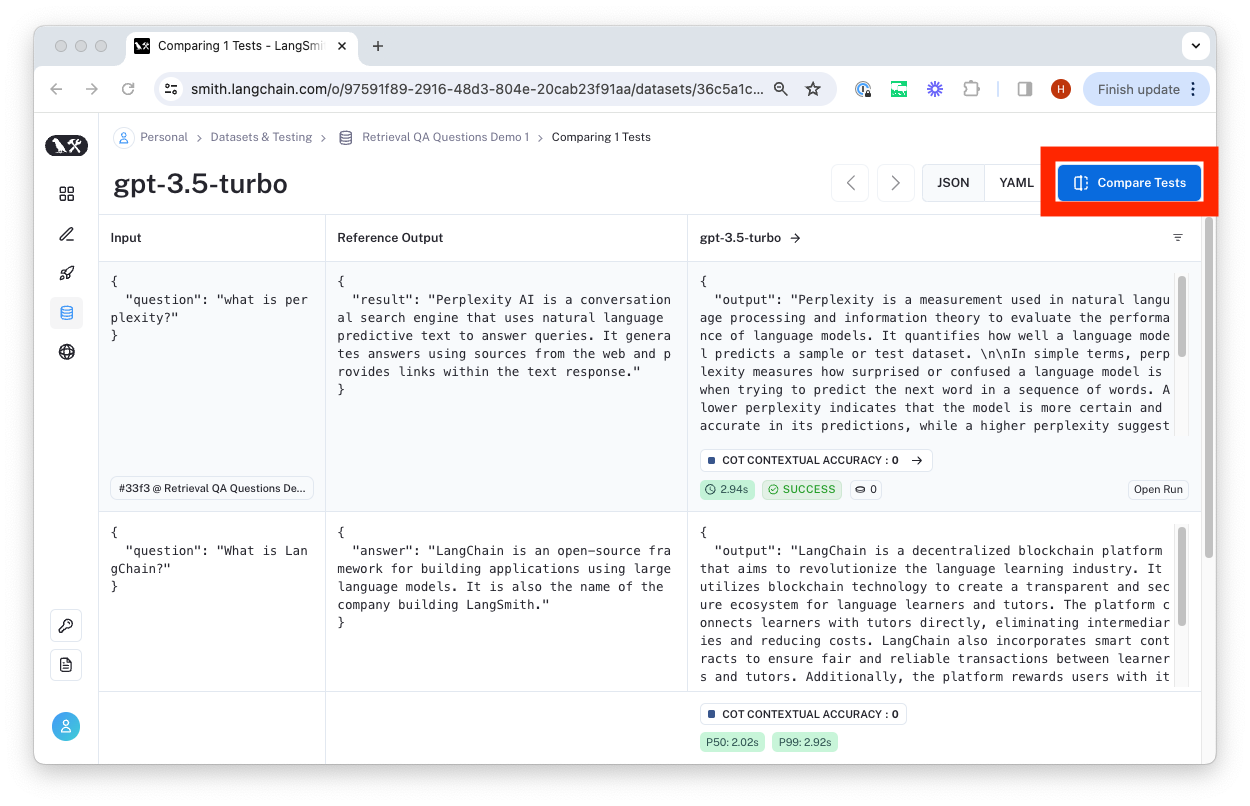
To compare to another test on this dataset, you can click "Compare Tests".
More on evaluation
Congratulations! You've now created a dataset and used it to evaluate your agent or LLM. To learn more about evaluation chains available out of the box, check out the LangChain Evaluators guide. To learn how to make your own custom evaluators, review the Custom Evaluator guide.